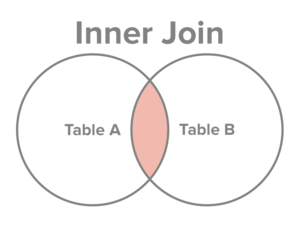
Источник: sql-join.com

Select all records from Table A and Table B, where the join condition is met.
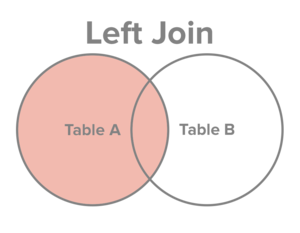
Select all records from Table A, along with records from Table B for which the join condition is met (if at all).
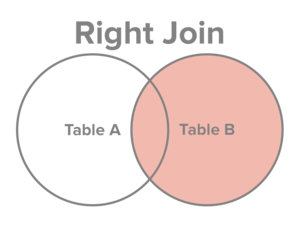
Select all records from Table B, along with records from Table A for which the join condition is met (if at all).
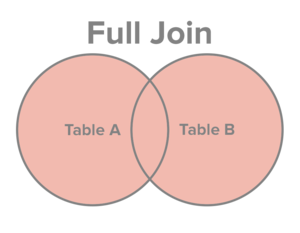
Select all records from Table A and Table B, regardless of whether the join condition is met or not.
Let’s use the tables we introduced in the “What is a SQL join?” section to show examples of these joins in action. The relationship between the two tables is specified by the customer_id key, which is the “primary key” in customers table and a “foreign key” in the orders table:
Table 1
| customer_id | first_name | last_name | address | city | state | zipcode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | George | Washington | [email protected] | 3200 Mt Vernon Hwy | Mount Vernon | VA | 22121 |
| 2 | John | Adams | [email protected] | 1250 Hancock St | Quincy | MA | 2169 |
| 3 | Thomas | Jefferson | [email protected] | 931 Thomas Jefferson Pkwy | Charlottesville | VA | 22902 |
| 4 | James | Madison | [email protected] | 11350 Constitution Hwy | Orange | VA | 22960 |
| 5 | James | Monroe | [email protected] | 2050 James Monroe Parkway | Charlottesville | VA | 22902 |
Table 2
| order_id | order_date | amount | customer_id |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | July 4, 1776 | 234.56 | 1 |
| 2 | March 14, 1760 | 78.5 | 3 |
| 3 | May 23, 1784 | 124 | 2 |
| 4 | September 3, 1790 | 65.5 | 3 |
| 5 | July 21, 1795 | 25.5 | 10 |
| 6 | November 27, 1787 | 14.4 | 9 |